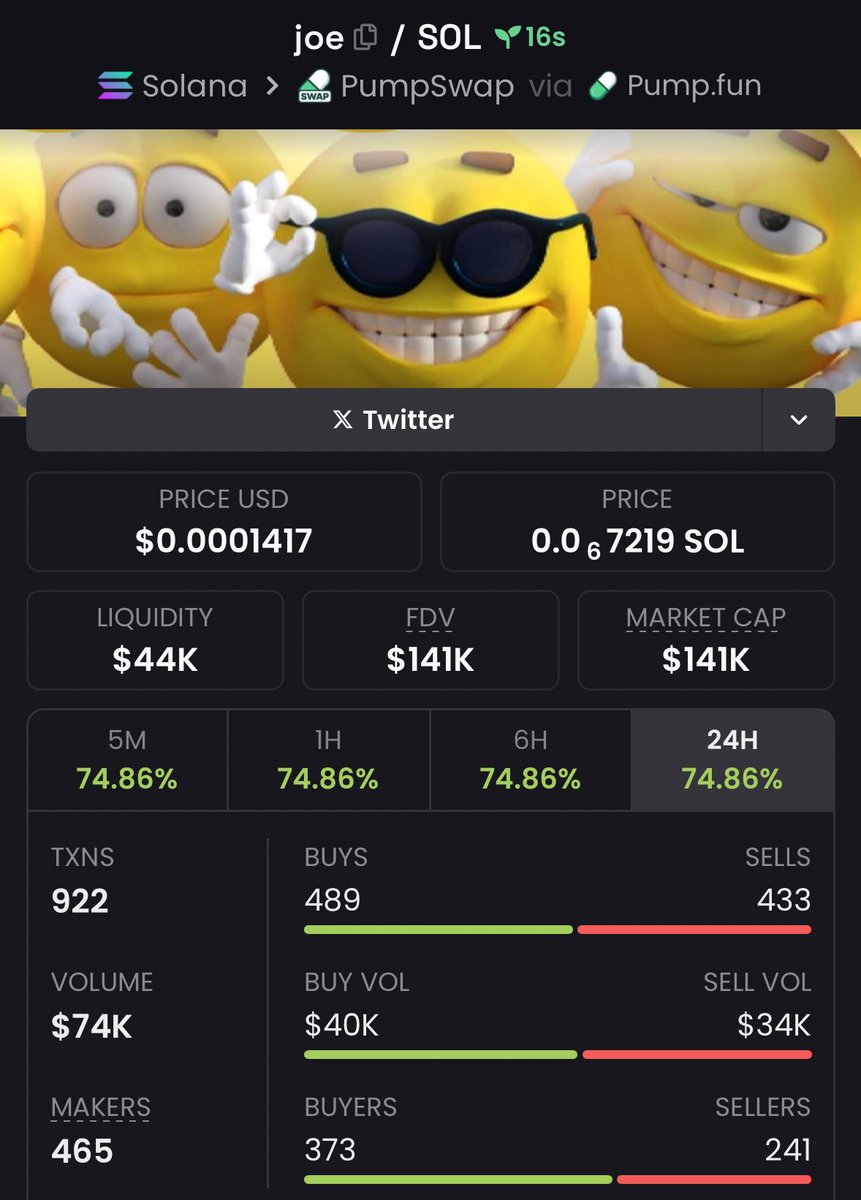
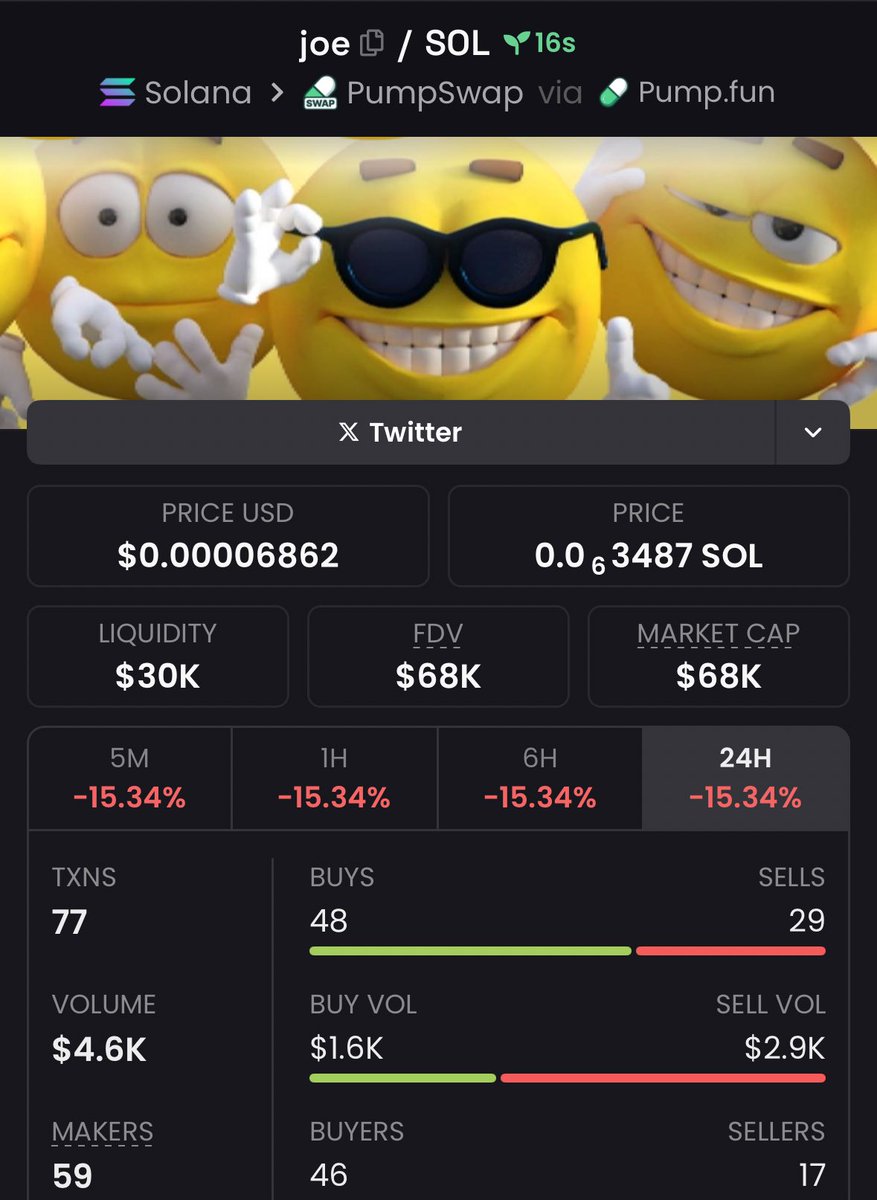
Preț JOE
în EUR

Despre JOE
Riscul asociat emitentului JOE
Limitarea răspunderii
OKX nu furnizează recomandări privind investițiile sau activele. Trebuie să analizați cu atenție dacă să tranzacționați sau să dețineți activele digitale prin prisma stării dvs. financiare. Consultați-vă cu un profesionist în domeniul juridic / fiscal / de investiții pentru întrebări despre circumstanțele dumneavoastră specifice. Pentru detalii suplimentare, consultați Condițiile de utilizare și Avertizarea de risc. Prin utilizarea paginii web terțe („TPW”), acceptați că orice utilizare a unei TPW va fi supusă oricăror și guvernată de orice condiții pentru TPW. Exceptând mențiunile exprese în scris, OKX și afiliații săi („OKX”) nu sunt în niciun fel asociați cu proprietarul sau operatorul TPW. Sunteți de acord că OKX nu este responsabilă sau răspunzătoare pentru nicio pierdere, daună și orice alte consecințe care decurg din utilizarea de către dumneavoastră a unei TPW. Țineți cont că utilizarea TPW poate duce la pierderea sau diminuarea activelor dumneavoastră. Este posibil ca produsul să nu fie disponibil în toate jurisdicțiile.
Performanța prețului pentru JOE
JOE pe rețelele sociale
Ghiduri

Întrebări frecvente JOE
Trader Joe este un schimb descentralizat (DEX) care operează pe blockchain-ul Avalanche și care oferă o gamă largă de servicii legate de DeFi, inclusiv împrumuturi, producerea și furnizarea de lichiditate. Acesta caută să fie o platformă cuprinzătoare pentru toate lucrurile DeFi, promovând accesibilitatea și intrarea egală pe piață prin interfața sa ușor de utilizat. În ciuda faptului că este relativ nou, Trader Joe a obținut un succes semnificativ, devenind cel mai mare AMM DEX cu cea mai mare valoare totală blocată (TVL) din ecosistemul Avalanche.
Deținerea tokenilor JOE oferă diverse avantaje utilizatorilor. Deținătorii de tokeni pot miza JOE pentru a câștiga monede stabile, oferind o oportunitate de venit pasiv. În plus, deținerea JOE permite utilizatorilor să participe la furnizarea de lichidități pentru fonduri, acordând privilegii de vot în cadrul comunității și promovând un sentiment de apartenență. Mai mult, JOE oferă acces la platforma de lansare Trader Joe, deblocând oportunități interesante pentru utilizatori de a se implica cu noi proiecte și inovații.
Cumpărați cu ușurință tokeni JOE pe platforma de criptomonede OKX. Perechea de tranzacționare disponibilă în terminalul de tranzacționare la vedere al OKX este JOE/USDT. De asemenea, puteți schimba criptomonedele existente, inclusiv Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT) și USD Coin (USDC), în JOE cu zero comisioane și fără alunecare de preț prin utilizarea OKX Convert.
Aflați mai multe despre JOE
Trader Joe (JOE) este un schimb descentralizat (DEX) de criptomonede care funcționează pe blockchain, oferind utilizatorilor o platformă perfectă pentru cumpărarea și vânzarea de active digitale. Ca DEX, Trader Joe oferă un mediu de tranzacționare descentralizat și sigur, fără intermediari sau autorități centrale. Acest lucru oferă utilizatorilor control complet asupra activelor lor și promovează o experiență de tranzacționare mai transparentă și fără încredere.
Ce este Trader Joe?
Trader Joe este un schimb descentralizat (DEX) care operează în rețeaua Avalanche, oferind o gamă largă de servicii de finanțe descentralizate (DeFi), inclusiv stakingul, producerea randamentului și tranzacționarea. Acesta își propune să fie un ghișeu unic și cuprinzător pentru diverse oferte DeFi, cum ar fi credite/împrumuturi, fonduri de lichiditate, platforme de lansare și tokeni nefungibili (NFT-uri). Cu interfața sa ușor de utilizat, Trader Joe este un creator de piață automatizat (AMM), ceea ce face accesibil și convenabil pentru utilizatori să participe la activitățile DeFi.
Echipa Trader Joe
Echipa Trader Joe rămâne anonimă, platforma fiind lansată în 2021 de către fondatori cunoscuți sub pseudonimele Cryptofish și OxMurloc. Cryptofish este descris ca un inginer de contracte inteligente și un colaborator timpuriu la mai multe proiecte din rețeaua Avalanche. OxMurloc pretinde că este un dezvoltator full-stack cu experiență, cu experiență în crearea de start-up-uri. Pe lângă fondatori, Trader Joe beneficiază de o echipă de dezvoltatori, comercianți și agenți de marketing calificați.
Cum funcționează Trader Joe?
Trader Joe combină creditarea, DEX-ul și tranzacționarea medie. Este primul care implementează ordine limită, ceea ce ajută la eliminarea alunecării de preț, care este una dintre cele mai frecvente probleme a DEX-urilor. Platforma oferă servicii de tranzacționare și schimb, precum și alte opțiuni legate de DeFi, cum ar fi producerea randamentului, împrumutul și stakingul.
JOE: Tokenul nativ Trader Joe
JOE este tokenul nativ al schimbului descentralizat (DEX) Trader Joe. Spre deosebire de alte DEX-uri, Trader Joe oferă o multitudine de cazuri de utilizare pentru tokenul său, făcându-l un element fundamental al proiectului. JOE joacă un rol crucial în fondurile de lichiditate, permițând utilizatorilor să adauge sau să retragă lichiditate din fondurile existente.
În plus, servește ca un activ de staking, facilitează împrumutul și acționează ca un token de guvernanță. Deținătorii de JOE se bucură de drepturi de vot, permițându-le să participe activ la modelarea viitorului DEX prin luarea de recomandări și decizii.
Tokenomia JOE
JOE are o aprovizionare maximă de 500 de milioane de tokeni, cu o aprovizionare circulantă de 341,48 milioane de tokeni. Tokenomia JOE permite utilizatorilor să se angajeze în activități de creditare și împrumut pe platforma Trader Joe. În plus, deținătorii de JOE vor avea acces la platforma de lansare integrată a proiectului.
Cazuri de utilizare JOE
JOE servește ca un token de guvernanță, acordând deținătorilor drepturi de vot în rețea. De asemenea, permite stakingul, permițând utilizatorilor să câștige recompense. JOE oferă acces la Trader Joe Launchpad. În plus, tokenul este utilizat în fondul de lichiditate, permițând servicii de creditare și împrumut pe platforma Trader Joe.
Distribuția JOE
JOE este distribuit după cum urmează:
- Cincizeci la sută sunt alocați furnizorilor de lichiditate.
- Douăzeci de procente sunt alocați pentru trezoreria Trader Joe.
- Douăzeci la sută sunt deținuți de echipa de dezvoltare.
- Zece la sută este rezervat viitorilor suporteri.
Ce rezervă viitorul pentru Trader Joe?
Trader Joe își propune să devină o platformă de schimb cuprinzătoare, combinând funcționalitățile DeFi și DEX. Echipa se angajează să îmbunătățească platforma prin integrarea mai multor instrumente, permițând tranzacționarea durabilă a randamentului și opțiunile avansate de producție pentru utilizatori. În plus, Trader Joe plănuiește să includă ordine limită și opțiuni de tranzacționare futures în oferta sa. Cu viteza, eficiența și interfața ușor de utilizat, platforma a atras susținători puternici în spațiu, inclusiv Stani Kulechov, fondatorul AAVE (AVVE). Viitorul pare promițător pentru Trader Joe, deoarece continuă să evolueze și să-și extindă serviciile în spațiul DeFi.
Raportare privind gazele cu efect de seră